If you’re concerned about fall risks and want to ensure the safety of yourself or your loved ones, you may be wondering, “What is the best fall risk assessment tool?” Fall prevention is crucial, especially for older adults, as falls can lead to serious injuries. Fortunately, there are various tools available to assess and mitigate fall risks. In this article, we’ll explore the top fall risk assessment tools and help you find the best one for your needs.
When it comes to fall risk assessment, it’s important to choose a tool that is accurate, comprehensive, and easy to use. With so many options available, it can be overwhelming to determine which tool is the most effective. That’s where we come in! We’ve done the research and compiled a list of the best fall risk assessment tools on the market. So, whether you’re a healthcare professional looking for a tool to use in your practice or an individual looking to assess your own fall risk, keep reading to discover the top options available.
When it comes to fall risk assessment tools, there are several options available. One highly recommended tool is the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test. This test measures the time it takes for a person to stand up from a chair, walk a short distance, turn around, and sit back down. It is a simple yet effective way to assess balance and mobility, which are key factors in fall risk. Other commonly used fall risk assessment tools include the Berg Balance Scale and the Morse Fall Scale. Ultimately, the best tool for fall risk assessment may vary depending on the individual’s needs and circumstances.
What is the Best Fall Risk Assessment Tool?
Fall prevention is a critical aspect of healthcare, particularly for older adults who are more susceptible to falls and their associated injuries. To effectively prevent falls, healthcare professionals rely on fall risk assessment tools. These tools help identify individuals who are at a higher risk of falling, allowing healthcare providers to implement appropriate preventive measures. With a wide range of fall risk assessment tools available, it can be challenging to determine which one is the best fit for a particular healthcare setting or individual. In this article, we will explore various fall risk assessment tools and discuss their features, benefits, and limitations.
1. The Timed Up and Go Test
The Timed Up and Go (TUG) test is a commonly used fall risk assessment tool. It measures the time it takes for an individual to stand up from a chair, walk a short distance, turn around, walk back to the chair, and sit down again. The TUG test assesses an individual’s balance, mobility, and gait speed, providing valuable information about their fall risk. During the test, healthcare professionals observe the individual’s movements and note any difficulties or abnormalities.
The TUG test is a quick and simple tool that requires minimal equipment, making it suitable for various healthcare settings. It has been validated in multiple studies and is widely recognized as a reliable fall risk assessment tool. However, it is essential to consider that the TUG test primarily focuses on mobility and may not capture other factors contributing to fall risk, such as muscle weakness or cognitive impairments.
Benefits of the TUG Test
One of the key benefits of the TUG test is its simplicity and ease of administration. It can be performed in a matter of minutes and does not require specialized equipment, making it accessible to healthcare professionals in different settings. Additionally, the TUG test provides valuable information about an individual’s balance and mobility, helping healthcare providers tailor interventions to reduce fall risk.
However, it is important to note that the TUG test is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to fall risk assessment. It should be used in conjunction with other assessment tools and clinical judgment to obtain a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s fall risk profile.
2. The Berg Balance Scale
The Berg Balance Scale (BBS) is a widely used fall risk assessment tool that evaluates an individual’s balance and functional mobility. It consists of 14 different tasks, including standing up from a sitting position, reaching for objects, and maintaining balance in various positions. Each task is scored on a scale of 0 to 4, with a total possible score of 56. Higher scores indicate better balance and lower fall risk.
The BBS is often used in rehabilitation settings to assess individuals recovering from injuries or surgeries that affect their balance. It provides detailed information about specific balance deficits and can guide the development of targeted interventions. However, the BBS may be less suitable for individuals with severe cognitive impairments or those who are unable to perform the required tasks due to physical limitations.
Benefits of the Berg Balance Scale
One of the main advantages of the BBS is its comprehensive assessment of balance and functional mobility. By evaluating various tasks, it provides a more detailed understanding of an individual’s balance deficits and fall risk factors. The BBS is also widely recognized and has been extensively validated, making it a reliable tool for fall risk assessment.
However, it is important to consider that the BBS may not be suitable for all individuals, particularly those with severe cognitive impairments or significant physical limitations. In such cases, alternative assessment tools should be utilized to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of fall risk.
3. The Morse Fall Scale
The Morse Fall Scale is a fall risk assessment tool that incorporates six different factors to determine an individual’s fall risk level. These factors include history of falling, secondary diagnosis, ambulatory aids, intravenous therapy, gait, and mental status. Each factor is assigned a score, and the scores are summed to provide an overall fall risk score. Higher scores indicate a higher risk of falling.
The Morse Fall Scale is commonly used in hospitals and other acute care settings to assess patients’ fall risk upon admission. It helps healthcare providers identify individuals who require additional fall prevention measures, such as bed alarms, increased supervision, or mobility aids. However, it is important to note that the Morse Fall Scale is primarily designed for use in acute care settings and may not be as effective in other healthcare settings or for long-term fall risk assessment.
Benefits of the Morse Fall Scale
The Morse Fall Scale offers a comprehensive assessment of various fall risk factors, providing healthcare providers with a holistic view of an individual’s fall risk. It helps identify individuals who require additional preventive measures to ensure their safety. The simplicity of the scale and its widespread use in acute care settings make it a practical tool for fall risk assessment.
However, it is crucial to consider that the Morse Fall Scale may not capture all factors contributing to fall risk, particularly those related to long-term care or community-based settings. Supplementing the scale with other assessment tools and clinical judgment is essential for a comprehensive fall risk evaluation.
4. The Hendrich II Fall Risk Model
The Hendrich II Fall Risk Model is a fall risk assessment tool specifically designed for hospitalized adults. It incorporates eight different risk factors, including confusion, symptomatic depression, altered elimination, dizziness or vertigo, male gender, antiepileptic medications, benzodiazepines, and nonuse of mobility aids. Each risk factor is assigned a score, and the scores are summed to provide an overall fall risk score. Higher scores indicate a higher risk of falling.
The Hendrich II Fall Risk Model helps healthcare providers identify individuals who require additional fall prevention measures during their hospital stay. It allows for targeted interventions, such as increased supervision, bed alarms, or assistive devices, to mitigate fall risk. However, it is important to note that the Hendrich II Fall Risk Model is specifically designed for use in hospitalized adults and may not be as effective in other healthcare settings.
Benefits of the Hendrich II Fall Risk Model
One of the main benefits of the Hendrich II Fall Risk Model is its specificity to the hospital setting. It takes into account factors that are particularly relevant to hospitalized adults, allowing healthcare providers to tailor interventions accordingly. The model’s simplicity and ease of use make it a practical tool for fall risk assessment in acute care settings.
However, it is crucial to consider that the Hendrich II Fall Risk Model may not be as effective in other healthcare settings or for long-term fall risk assessment. Healthcare providers should supplement the model with other assessment tools and clinical judgment to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of fall risk.
5. The Tinetti Performance-Oriented Mobility Assessment
The Tinetti Performance-Oriented Mobility Assessment (POMA) is a comprehensive fall risk assessment tool that evaluates an individual’s balance and gait. It consists of two main components: the gait assessment and the balance assessment. The gait assessment evaluates an individual’s walking pattern, while the balance assessment assesses their ability to maintain balance in various positions and during specific tasks.
The Tinetti POMA provides a detailed evaluation of an individual’s balance and gait, helping healthcare providers identify specific deficits and fall risk factors. It is often used in geriatric settings and has been extensively validated in older adults. However, it is important to consider that the Tinetti POMA may be more time-consuming to administer compared to other fall risk assessment tools.
Benefits of the Tinetti Performance-Oriented Mobility Assessment
One of the main advantages of the Tinetti POMA is its comprehensive assessment of balance and gait. By evaluating specific tasks and movements, it provides detailed information about an individual’s fall risk factors. The Tinetti POMA is widely recognized and has been extensively validated in older adults, making it a reliable tool for fall risk assessment in geriatric settings.
However, it is essential to consider the time required to administer the Tinetti POMA, particularly in busy healthcare settings. Healthcare providers should assess the feasibility of using the tool and consider alternative assessment options if necessary.
Additional Considerations for Fall Risk Assessment
In addition to the specific fall risk assessment tools mentioned above, there are several other factors that healthcare providers should consider when evaluating an individual’s fall risk. These include:
– Medical history: Assessing an individual’s medical history, including previous falls, chronic conditions, and medications, can provide valuable insights into their fall risk.
– Environmental factors: Evaluating the individual’s living environment, including home safety measures and potential fall hazards, is crucial for fall risk assessment.
– Functional status: Assessing an individual’s functional abilities, such as their ability to perform activities of daily living, can help identify potential fall risk factors.
– Cognitive status: Evaluating an individual’s cognitive function and mental status is essential, as cognitive impairments can increase fall risk.
– Muscle strength and balance: Assessing an individual’s muscle strength and balance through specific tests or assessments can provide valuable information about their fall risk.
By considering these additional factors in conjunction with the appropriate fall risk assessment tools, healthcare providers can develop tailored fall prevention strategies and interventions. It is important to remember that fall risk assessment is an ongoing process, and regular reassessment is essential to ensure the effectiveness of preventive measures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fall risk assessment tools play a crucial role in identifying individuals who are at a higher risk of falling. The Timed Up and Go test, the Berg Balance Scale, the Morse Fall Scale, the Hendrich II Fall Risk Model, and the Tinetti Performance-Oriented Mobility Assessment are just a few examples of the tools available. Each tool has its own unique features, benefits, and limitations, and healthcare providers should consider various factors when selecting the most appropriate tool for fall risk assessment. By utilizing these tools in conjunction with a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s medical history, environmental factors, functional status, cognitive status, and muscle strength and balance, healthcare providers can effectively prevent falls and promote the safety and well-being of their patients.
Key Takeaways: What is the Best Fall Risk Assessment Tool?
- 1. A fall risk assessment tool helps determine a person’s risk of falling.
- 2. The best fall risk assessment tool is one that is evidence-based and validated.
- 3. The tool should consider various factors such as age, medical history, and mobility.
- 4. Common fall risk assessment tools include the Timed Up and Go Test and the Berg Balance Scale.
- 5. Consulting with healthcare professionals can help identify the most suitable fall risk assessment tool for an individual.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors should be considered when choosing a fall risk assessment tool?
When choosing a fall risk assessment tool, there are several factors to consider. First, consider the population you will be assessing. Are you working with older adults, patients in a hospital setting, or individuals with specific medical conditions? Different tools may be more appropriate for different populations.
Second, consider the validity and reliability of the tool. It’s important to choose a tool that has been tested and shown to accurately assess fall risk. Look for studies or evidence supporting the tool’s effectiveness.
What are some commonly used fall risk assessment tools?
There are several commonly used fall risk assessment tools that have been widely studied and validated. The Timed Up and Go (TUG) test is a simple and quick assessment that measures the time it takes for an individual to stand up from a chair, walk a short distance, turn around, and sit back down. The Berg Balance Scale is another widely used tool that assesses an individual’s balance and risk of falling.
Other tools include the Morse Fall Scale, the Hendrich II Fall Risk Model, and the STRATIFY tool. Each tool has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it’s important to consider the specific needs of your population when choosing a tool.
Are there any online fall risk assessment tools available?
Yes, there are online fall risk assessment tools available. These tools can be convenient for healthcare professionals who want to quickly assess fall risk without the need for physical paperwork. One example is the Fall Prevention Toolkit, which includes an online fall risk assessment tool that can be completed by the patient or caregiver.
However, it’s important to note that online tools may not be as comprehensive as in-person assessments. They may not take into account certain physical or environmental factors that can contribute to fall risk. It’s always best to use online tools as a starting point and follow up with a more thorough assessment if needed.
What are the benefits of using a fall risk assessment tool?
Using a fall risk assessment tool can provide several benefits. First and foremost, it helps healthcare professionals identify individuals who are at risk of falling. This allows for targeted interventions and preventive measures to be implemented, reducing the likelihood of falls and related injuries.
Additionally, fall risk assessment tools can help track changes in an individual’s fall risk over time. By regularly assessing fall risk, healthcare professionals can monitor the effectiveness of interventions and adjust treatment plans accordingly. This proactive approach can lead to better outcomes and improved patient safety.
Can fall risk assessments be done by non-medical professionals?
While fall risk assessments are typically performed by healthcare professionals, there are certain tools that can be used by non-medical professionals as well. These tools are designed to be user-friendly and require minimal training to administer.
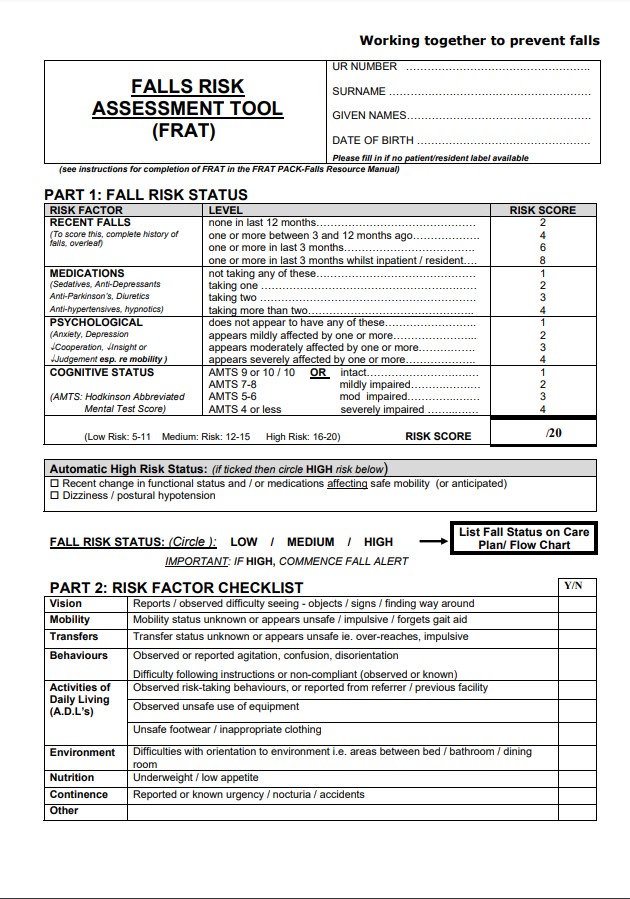
For example, the Falls Risk Assessment Tool (FRAT) is a simple questionnaire that can be completed by non-medical individuals, such as caregivers or family members. It asks a series of questions about the individual’s mobility, balance, and previous falls to determine their risk of falling. However, it’s important to remember that these assessments should always be used in conjunction with professional medical advice and supervision.

Final Summary: The Best Fall Risk Assessment Tool for Ensuring Safety
After exploring various fall risk assessment tools, it is clear that finding the best one depends on the specific needs and requirements of the individual. Each tool offers unique features and benefits that cater to different scenarios and settings. However, there are a few standout options that consistently rank high in terms of effectiveness and reliability.
One such tool is the “ABC Test,” which assesses an individual’s agility, balance, and coordination. This comprehensive assessment provides valuable insights into a person’s physical capabilities and helps identify potential areas of improvement. Another notable tool is the “Timed Up and Go Test,” which measures the time it takes for someone to stand up from a chair, walk a short distance, turn around, and sit back down. This simple yet effective test is widely used in clinical settings and provides a quick assessment of mobility and fall risk.
Additionally, the “Berg Balance Scale” is highly regarded for its ability to accurately evaluate balance and stability. This test consists of a series of tasks designed to assess an individual’s ability to maintain their center of gravity while performing various movements. It is a reliable tool for identifying balance deficits and determining appropriate interventions.
While these are just a few examples, it is crucial to remember that the best fall risk assessment tool ultimately depends on the specific circumstances and needs of the individual. Consulting a healthcare professional or specialist is essential for determining the most suitable assessment tool for each unique situation. By prioritizing safety and utilizing the appropriate assessment tools, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent falls and maintain their well-being.
Remember, when it comes to fall risk assessment, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. It is crucial to consider individual factors, consult with experts, and choose the tool that best aligns with the specific needs of those at risk. By incorporating these assessments into regular care routines, we can work towards a safer and more secure future for individuals vulnerable to falls. Stay informed, take action, and prioritize safety for a life free from fall-related risks.